226.翻转二叉树
link
翻转一颗二叉树
思路 前序遍历或者后续遍历,在访问当前节点的时候就翻转节点的两个子树。
递归写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution: def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def treverse(node): if node != None: temp = node.right node.right = node.left node.left = temp treverse(node.left) treverse(node.right) treverse(root) return root
迭代写法(统一的思路)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution: def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: stack = [] if root != None: stack.append(root) while stack: cur = stack.pop() if cur != None: # 右节点入栈 if cur.right: stack.append(cur.right) # 左节点入栈 if cur.left: stack.append(cur.left) # 中间节点入栈 stack.append(cur) stack.append(None) else: cur = stack.pop() temp = cur.left cur.left = cur.right cur.right = temp return root
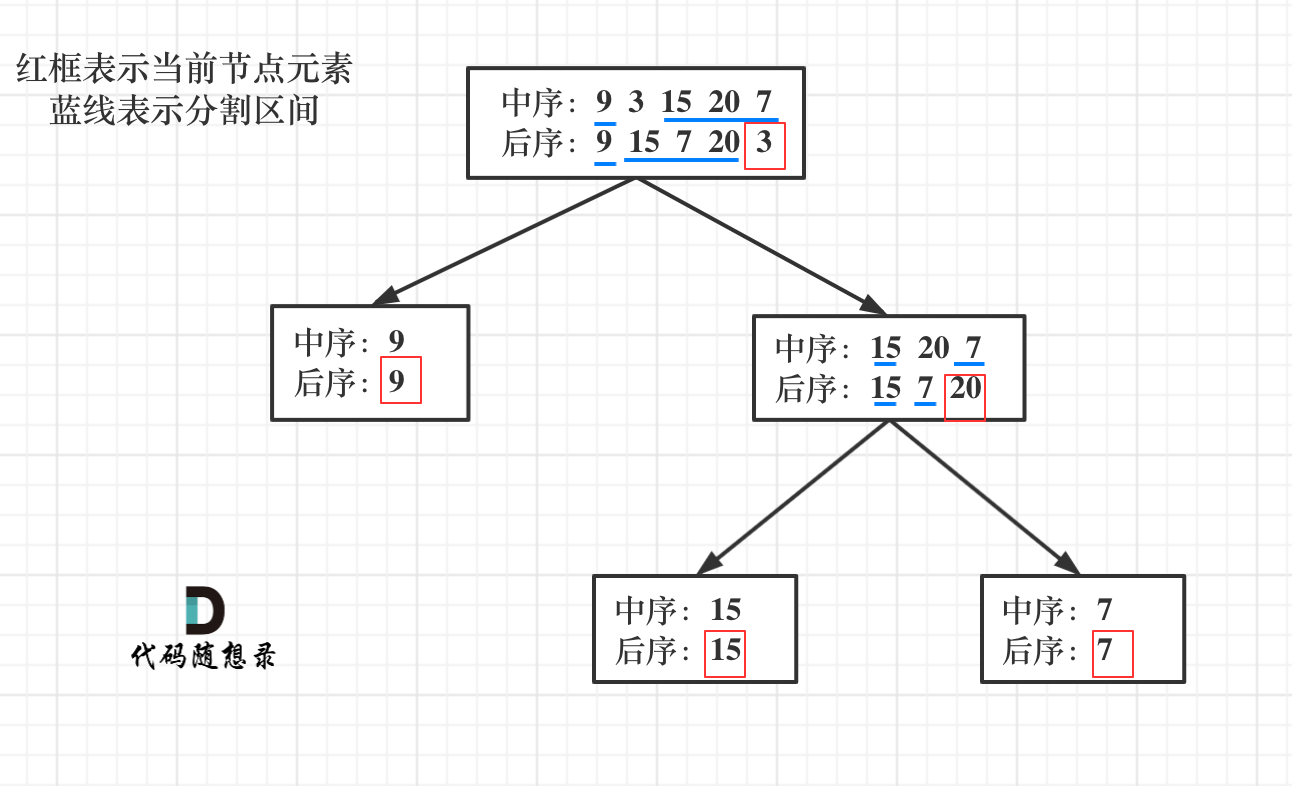
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
link
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
思路 明确:
后序遍历的性质:后序遍历的最后一个元素一定是整棵树的根节点。即 postorder = [左子树…, 右子树…, 根]
中序遍历的性质:在中序遍历中,根节点左边的元素是左子树,右边的是右子树。
过程如下:
从后序遍历中取出最后一个元素作为根节点;
在中序遍历中找到这个根节点的位置;
递归构建左右子树:
中序左边部分 → 左子树
中序右边部分 → 右子树
后序中要对应分成左子树和右子树的区间
注意在递归中,要优先处理右子树,因为右子树更靠近根节点,需要先 pop(但是为什么不需要手动切片?这里的 posto 不是局部变量吗?)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution: def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def make(ino, posto): if not ino or not posto: return None val = posto.pop() index = ino.index(val) root = TreeNode(val) subinleft = ino[0:index] subinright = ino[index+1:] root.right = make(subinright, posto) root.left = make(subinleft, posto) return root return make(inorder, postorder)
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
link
类似于上一题,只不过由于前序遍历是根节点在索引 0,无法动态更新数组,所以需要进行手动切片,此时就不需要在乎先处理哪个子树了,因为已经显示地指定。上一题需要先处理右子树,是因为需要在递归的过程中多次修改 posto 数组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution: def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def make(ino, posto): if not ino or not posto: return None val = posto[0] index = ino.index(val) root = TreeNode(val) subinleft = ino[0:index] subinright = ino[index+1:] root.left = make(subinleft, posto[1:len(subinleft)+1]) root.right = make(subinright, posto[len(subinleft)+1:]) return root return make(inorder, preorder)
小总结
前序和中序可以唯一确定一棵二叉树。
后序和中序可以唯一确定一棵二叉树。
但是前序和后序不能 唯一确定一棵二叉树!
因为无法确定根节点,就无法进行分割
654.最大二叉树
link
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
思路 类似于构造二叉树,思路在题目中已经给出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution: def constructMaximumBinaryTree(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def make(num_list): if not num_list: return None max_num = max(num_list) index = num_list.index(max_num) root = TreeNode(max_num) root.left = make(num_list[:index]) root.right = make(num_list[index+1:]) return root return make(nums)
617.合并二叉树
link
同时遍历两颗树即可。注意递归的主逻辑判断,当一个节点为空时,直接返回另一个节点,不用考虑另一个节点是否为空。只有两个节点都不为空的时候才需要单独判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution: def mergeTrees(self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]: def make(node1, node2): if node1 == None: return node2 if node2 == None: return node1 cur = TreeNode(node1.val + node2.val) cur.left = make(node1.left, node2.left) cur.right = make(node1.right, node2.right) return cur return make(root1, root2)